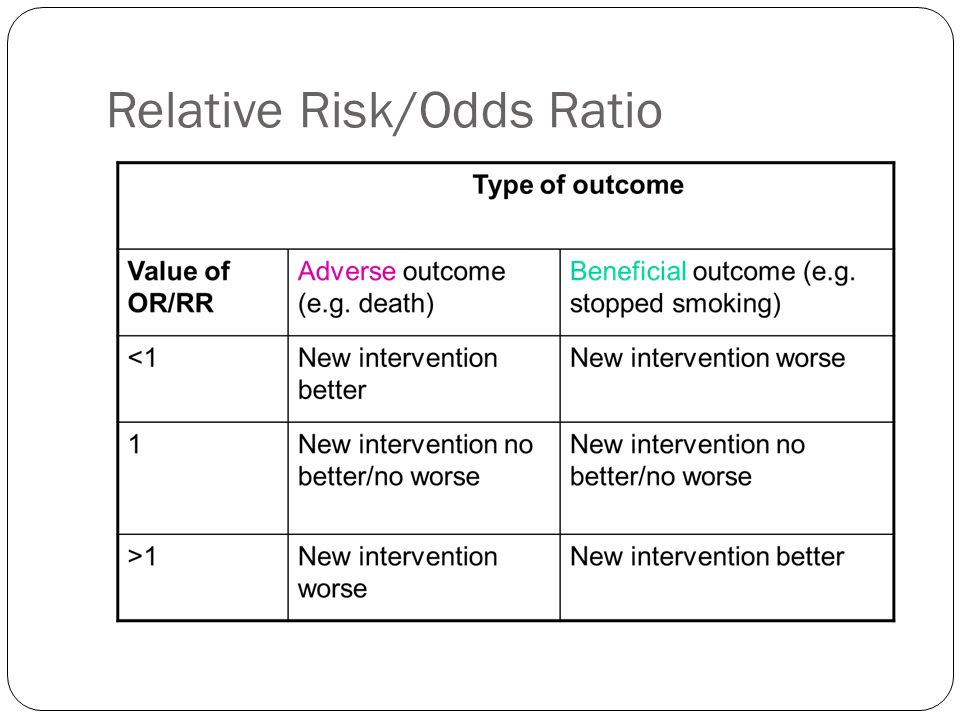
In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk; After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the studyBoth the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio

A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine
Odd ratio and relative risk calculation
Odd ratio and relative risk calculation-2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter Standard reporting practice is to report the odds ratio in terms of the incidence of the adverse event (death), and both the odds and risk ratios relative to the control condition;




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood
Risk Ratio = Rate1/Rate2 Odds1 = present1/absent1 Odds2 = present2/absent2 Odds Ratio = Odds1/Odds2 Log Odds = natural logarithm of Odds RatioThe probability of PONV with no Drug X is 40/100 or 040 Therefore, the relative risk for PONV with Drug X vs PONV without Drug X is 0/040 = 05 Odds ratios are used instead of relative risk for casecontrol studies To be able to calculate relative risk, we compare the risks of outcome in different groupsERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi for
An odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratioFor estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the default When the study design allows for the calculation of a relative risk, it is the preferred measure as it is far more interpretable than an odds ratio The odds ratio is extremely important, however, as it is the only measure of effect that can be computed in a
The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,Relative Risk and Odds Ratio Calculator This Relative Risk and Odds Ratio calculator allows you to determine the comparative risk of the occurrence of a significant event (or outcome) for two groups For example, suppose the members of one group each eat a kilo of cheese every day, and the members of another group eat no cheese, and you have data for both groups on the Once we calculate the odds ratio and relative risk, we may also be interested in computing confidence intervals for these two metrics A 95% confidence interval for the odds ratio can be calculated using the following formula 95% CI for odds ratio = exp(ln(OR) – 196*SE(ln(OR))) to exp(ln(OR) – 196*SE(ln(OR)))



Interpreting Basic Statistics Ppt Video Online Download




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
Quote Relative Risk For casecontrol studies quote Odds Ratio Odds Ratio approximates Relative Risk for a rare disease in casecontrol studies For a crosssectional study one has a choice between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk 36 The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while aA value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To




Relative Risk Wikipedia
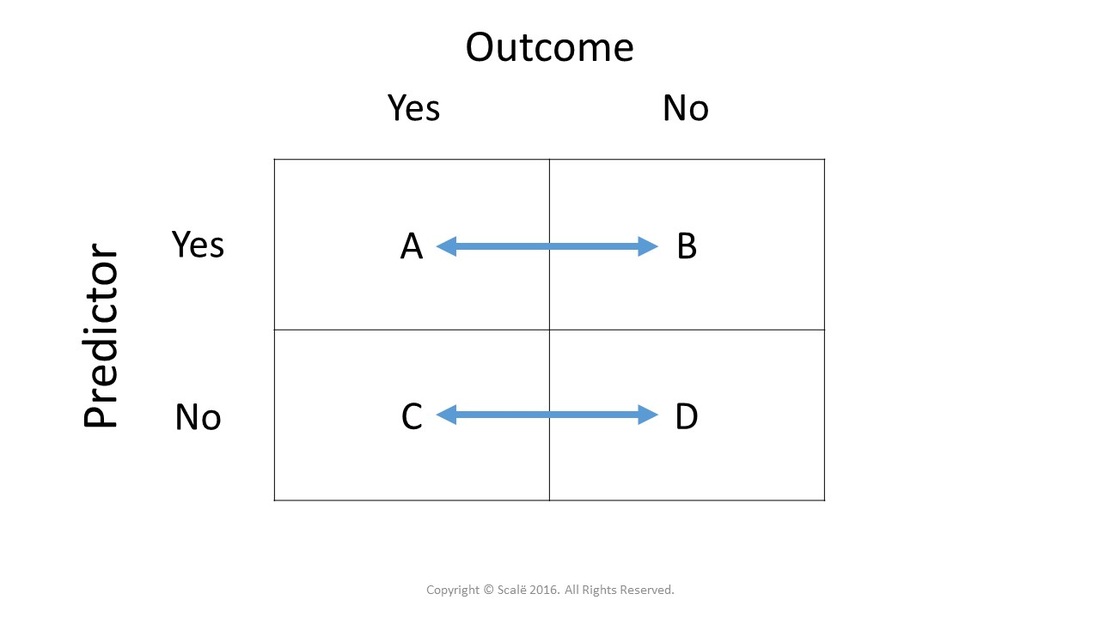
The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived From the data in the table 1, it is calculated as follows OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (152/17)/The risk ratio In practice, risks and odds for a single group are not nearly as interesting as a comparison of risks and odds between two groups For risk you can make these comparisons by dividing the risk for one group (usually the group exposed to the risk factor) by the risk for the second, nonexposed, group This gives us the risk ratio To calculate the risk ratio, first calculate the risk or attack rate for each group Here are the formulas Attack Rate (Risk) Attack rate for exposed = a ⁄ ab Attack rate for unexposed = c ⁄ cd For this example Risk of tuberculosis among East wing residents =




Odds Ratio Article




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine
In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable riskor risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposureRelative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) risk = odds/ (1odds) "Most published research providing an odds ratio as a measure of effect size should also provide sufficient information for the baseline risk, and hence the relative risk, to be calculated If numbers in each group are given, the crude relative risk can be calculated directly" – BMJ 14;348f7450 doi /bmj




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download



Relative Risk Odds Ratio
Relative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878 For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);Let us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
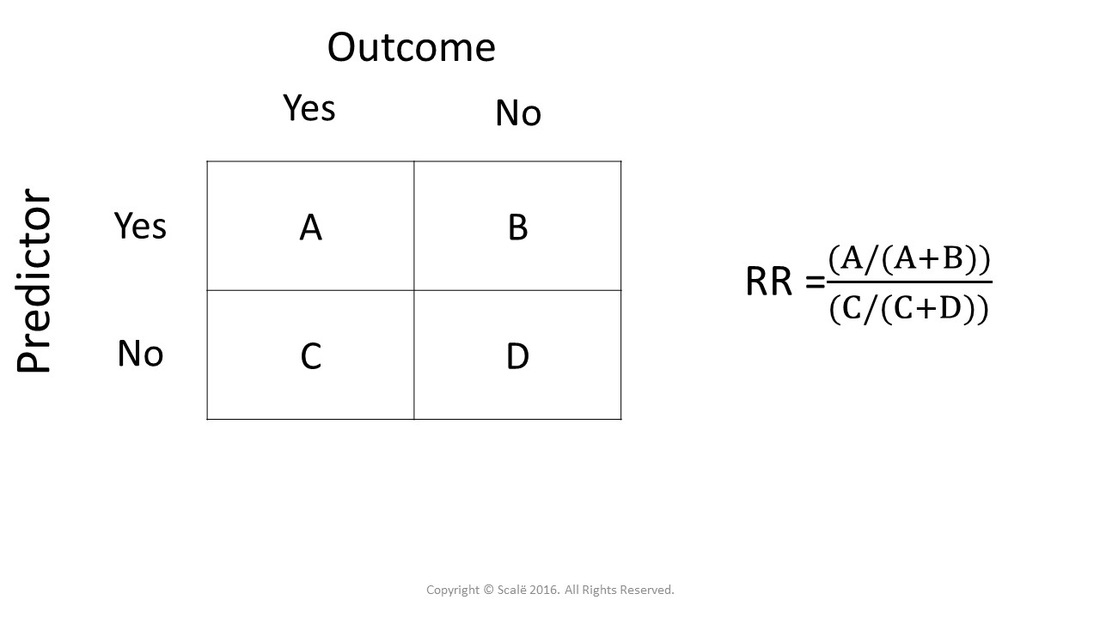
Thus the odds ratio is (a/b) / (c/d) which simplifies to ad/bc This is compared to the relative risk which is (a / (ab)) / (c / (cd)) If the disease condition (event) is rare, then the odds ratio and relative risk may be comparable, but the odds ratio will overestimate the risk ifOdds Ratio, Relative Risk, and Risk Difference How to Use Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, and Risk Difference to Describe the Association Between Two Categorical Risk Ratios and Rate Ratios (Relative Risk) Measures of disease frequency can be compared by calculating their ratio Common terms to describe these ratios are risk ratio rate ratio relative risk relative rate Frequently, the term "relative risk" is used to encompass all of these These relative measures give an indication of the "strength




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Random And Systematic Errors In Case Control Studies Calculating The Injury Risk Of Driving Under The Influence Of Psychoactive Substances Sciencedirect
Includes the 95% of risk ratios of these 100 population samples Thus, the 95% CI is the interval of values in which the true risk ratio is likely to lie with a probability of 95% To be statistically significant with a Po005, a risk ratio should have a 95% CI not including 10 Thus, in the HOPE study, the risk ratio of 078 (95% CI 070–0The odds ratio for lettuce was calculated to be 112 How would you interpret the odds ratio?OR* (ie, odds ratios relative to the average population) for each SNP can be Diabetes Risk Calculation Exercise Calculate the diabetes risk for 4 individuals using their genotype data using odds ratios vs likelihood ratios



Our Calculations Explained Cancer Research Uk




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
Ie, having the control condition appear in each ratio's denominator To conform to this standard, code the variables so that the Experimental, Died count is in the Odds ratio The Odds Ratio represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposure Its not the same as the relative risk reduction Consider a treatment trialSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj
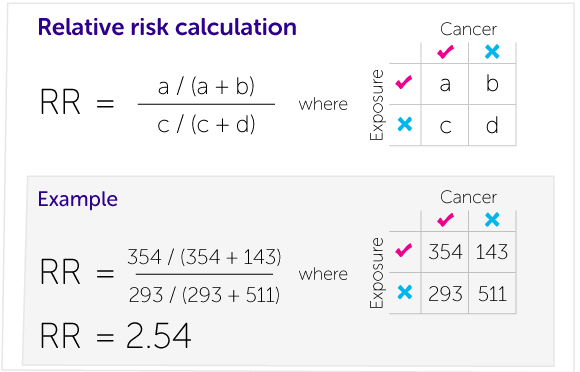
The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either ofAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higherThe simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variable




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)Relative Risk (RR) For a given disease, we can know the risk among exposed (r 1), and the risk among unexposed (r 0) Hence we can calculate the risk ratio as follows RR = r 1 / r 0 Similarly we can also calculate rate ratios if we know the rate of disease (rate of occurrence of new disease) in an exposed group (r 1), and the rate of disease The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the




Glossary Of Research Terminology




Sas Different Odds Ratio From Proc Freq Proc Logistic Stack Overflow
It's common to express a risk ratio as a percent increase when the risk ratio is greater than 1, and a percent decrease when the risk ratio is less than 1 Formulas for determining the percent increase or decrease are as follows Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an "exposed" group to develop aWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075



Logistic Regression Spss Annotated Output
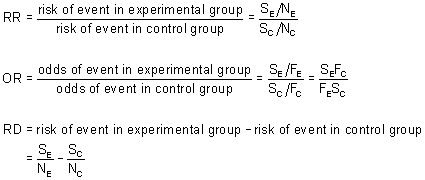



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd
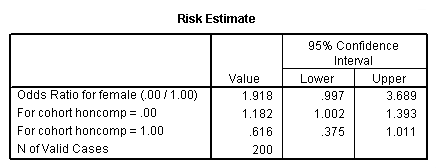
Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greater The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program




1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
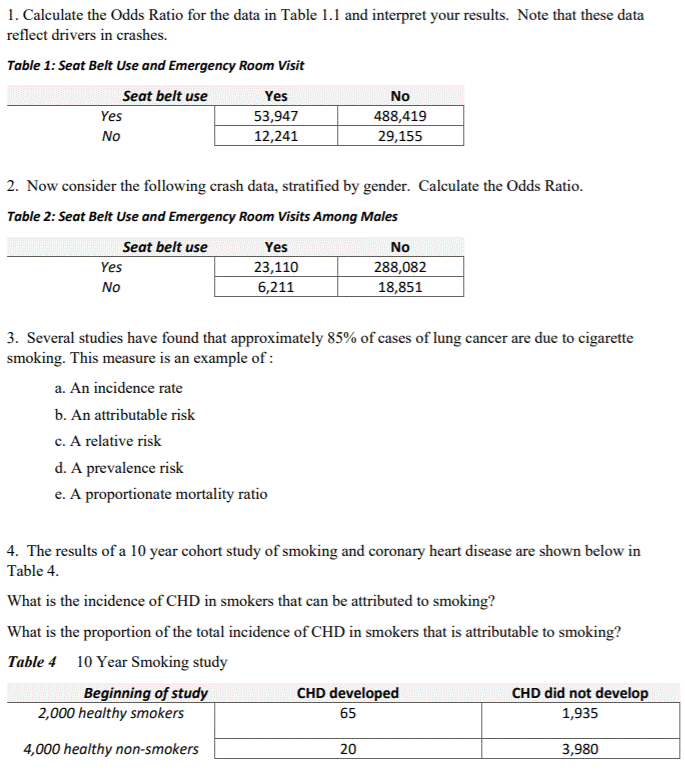



1 Calculate The Odds Ratio For The Data In Table 1 1 Chegg Com
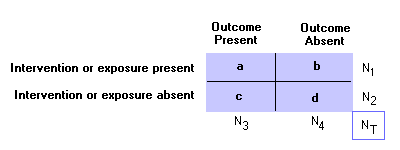



Epidemiology Glossary Physical Diagnosis Skills University Of Washington School Of Medicine



1



7 6 Vaccine Effectiveness Management Of A Measles Epidemic




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Critical Numbers Living With Risk Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
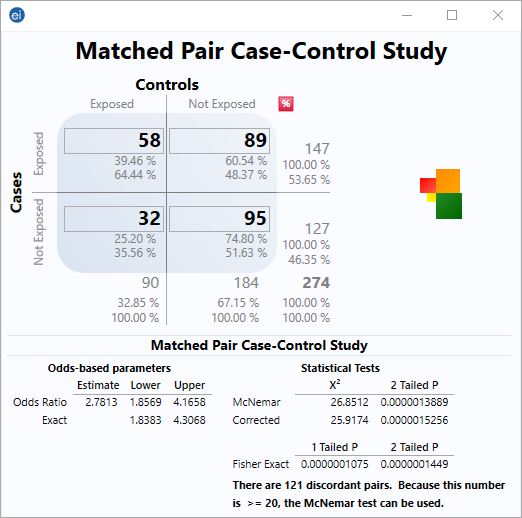



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Ch 12 Relative Risk Rr Or Flashcards Quizlet



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Absolute Relative And Attributable Risks Outcomes Or Differences That We Are Interested In Differences In Means Or Proportions Odds Ratio Or Ppt Download



Q Tbn And9gcs Pnxsjy3 X0gf842wm6tcfnesq2htc0kvu Tt2rst Svunqcb Usqp Cau




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Probability Lotto I Am Offered Two Lotto Cards




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau
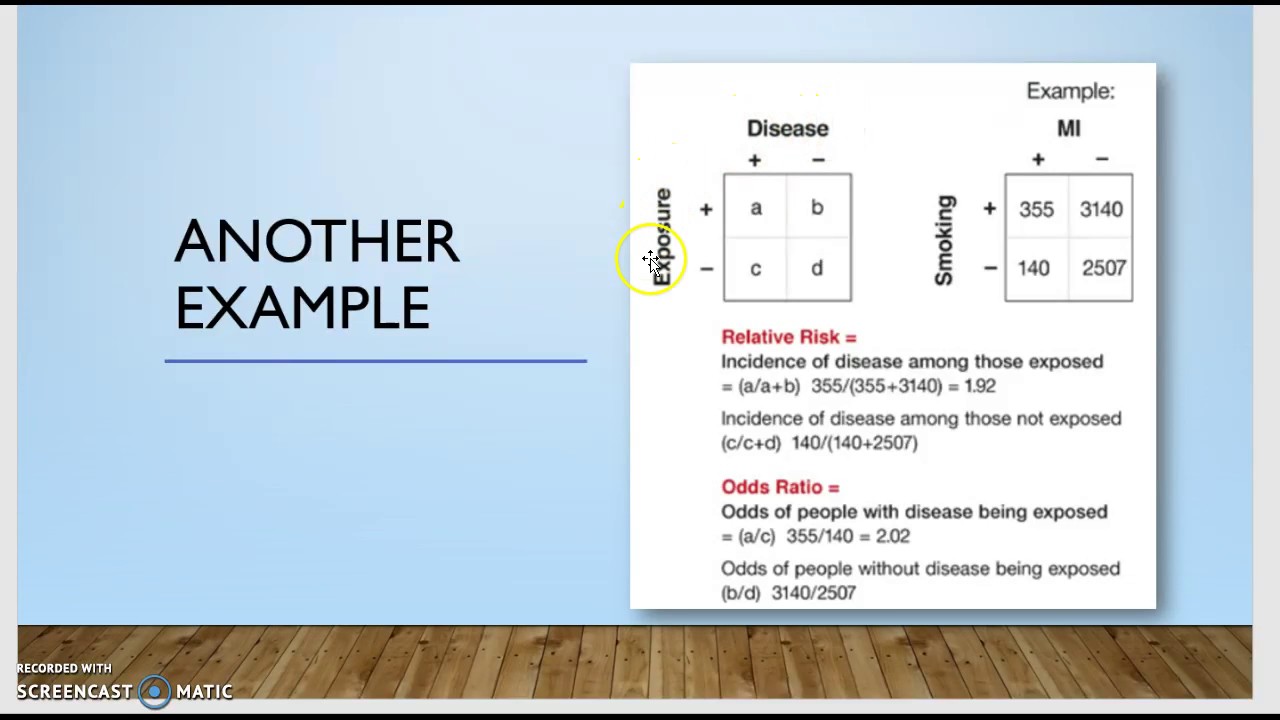



Calculating Relative Risk Odds Ratio And Rate Ratio Youtube
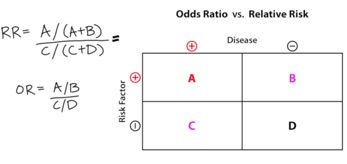



Behavioral Flashcards Memorang



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data




Relative Risk Calculator




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




A Most Odd Ratio Interpreting And Describing Odds Ratios Abstract Europe Pmc



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
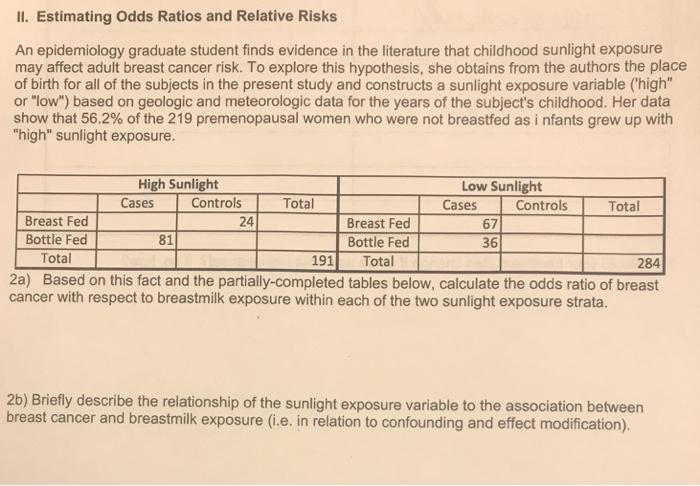



Il Estimating Odds Ratios And Relative Risks An E Chegg Com




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Estimating Risk




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh




Lecture3




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People




Measuring Of Risk




Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
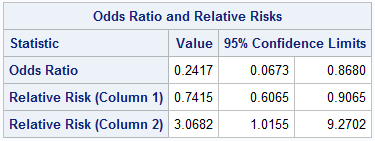



Statistics Basics Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Calculation In Excel Bi Practice



Atrium Lib Uoguelph Ca Xmlui Bitstream Handle 1873 B Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Pdf Sequence 8



Analytical Studies
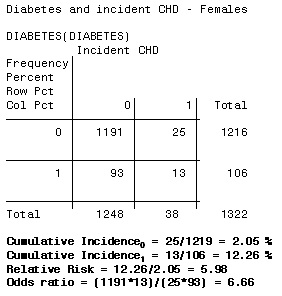



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau



Www Jstor Org Stable




The Relationship Between Nnt Calculated From An Odds Ratio Or And An Download Scientific Diagram
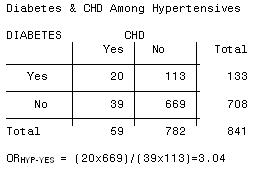



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
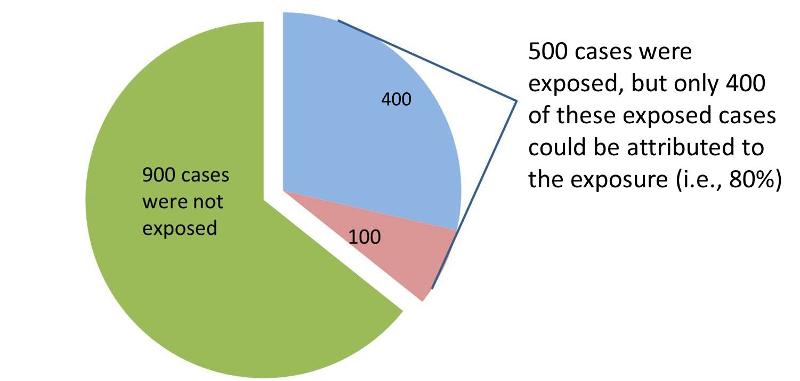



Measures Of Association



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿